Abstract
The effect of precursors on the characteristics of tin oxide obtained by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method was investigated. The synthesis of nanosized tin(IV) oxide was carried out with the use of two different precursors: tin(II) oxalate obtained using tin chloride(II) and oxalic acid; tin(II) oxalate obtained using tin chloride(II); and ammonium oxalate. The synthesized tin(IV) oxide samples were studied by electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and optical spectra. The lattice parameters of tin(IV) oxide samples were defined, the bandgap of samples were calculated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Metal oxides are the basis of modern diverse smart and functional materials and devices because physical and chemical properties of these oxides can be tuned.
Functional properties of metal oxides depends on many chemical and structural characteristics such as chemical composition, various kinds of deficiencies, morphology, particle size, surface-to-volume ratio, etc. By varying either of these characteristics, the electrical, optical, magnetic, and chemical properties can be regulated, giving the possibility of fabricating smart devices. Such unique characteristics make oxides the most diverse class of materials, with properties covering almost all aspects of materials science and physics in areas such as semiconductivity, superconductivity, ferroelectricity, and magnetism [1–4].
It is known that the reversible chemisorption of reactive gases on the surface of the oxide semiconductor is accompanied by reversible changes in conductivity. This makes semiconductors the most attractive materials for the manufacture photosensitive electronic converters based on them. Conductivity of semiconducting oxides caused by deviations from stoichiometry and also defects such as interstitial cation or anion vacancies. Depending on type of determinate impurity (electron acceptor or electron donor) and conduction type (n- or p-type), the resistance of the sensitive layer of the sensor is increased or decreased. Oxidizing gases or electron acceptors such as NO2 produce a decrease in the conductance of n-type semiconducting materials (i.e., electrons are the major carriers, such as ZnO, SnO2, In2O3) and an increase in the conductance of p-type semiconducting materials (i.e., holes are the major carriers, such as CuO); reducing gases or electron donors such as H2S, CO, H2 and water vapor act in a reverse manner [5, 6].
Metal oxides SnO2, ZnO, In2O3, and CdO are wide-bandgap n-type semiconductors and the most frequently used as a sensitive material for the gas sensors. They belong to a class of transparent conductive oxides due to a number of unique functional properties, of which the most important are the electrical conductivity, the visibility in a wide spectral range, and high reactivity of the surface [7, 8].
Metal oxide-based gas sensors are widely used due to its high sensitivity to harmful for human health or hazardous gases (such as CO, NO, NO2, H2, etc.) in conjunction with easy fabrication methods and low manufacturing costs. Tin(II) oxide is the promising sensor material among a wide set of semiconducting metal oxides [9–11]. It is known that nanocrystalline materials characterized the largest values of sensor response due to high surface-to-volume ratio and, therefore, higher absorption capacity [6].
To obtain nanocrystalline, SnO2 uses different methods: sol-gel method [12], chemical vapor deposition [13], hydrothermal [14], thermal evaporation [15]. Among a large number of approach methods of chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which is implemented of vapor-liquid-solid mechanism (VLS), deserves special attention. This method allows obtaining particles of very diverse morphology with a high degree of crystallinity [1, 16, 17]. In the articles [18–20], SnO2 nanowires and nanoribbons (doped and pure) have been successfully synthesized using such precursors as Sn and SnO2 powders. Also known to use other precursors for synthesis of SnO2 nanowires are SnO powder, and a mixture of carbon powder and SnO2 powder. However, from our point of view, it is interesting to research also other precursors, as has long been known that precursors have a significant impact on the final physicochemical properties of materials. In this paper, we investigate the effect of new precursor SnC2O4 (obtained from different reagents) on the characteristics of tin oxide obtained by CVD.
Methods of synthesis
Tin(II) oxalate was obtained by sol-gel method from different precursors: in the first case tin chloride(II) and oxalic acid; in the second case – tin chloride(II) and ammonium oxalate. In both cases, hot oxalic acid (ammonium oxalate) solution was added to hot aqueous solutions of SnCl2 · 2H2O in a molar ratio of 1:1.5, respectively. The resulting solution was cooled. The precipitate formed was filtered, washed with distilled water while ions Cl− detected by reaction with AgNO3 and dried in an oven at 378 K for 2 h. Thus, there were two obtained samples of tin oxalate: sample A – using oxalic acid and sample B – using ammonium oxalate (Table 1).
For tin(IV) oxide weighed tin(II) oxalate was loaded in an alumina boat, which was placed at the center of a quartz tube in a horizontal-type furnace. The furnace was heated to 1123, 1223, and 1323 K and kept in an inert atmosphere for 1 h. The inert atmosphere was implemented by nitrogen with 0.005 % oxygen impurity.
The overall reaction of tin(II) oxalate decomposition:
Obtained SnO2 samples (Table 2) were analyzed by electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and spectrophotometrically.
Results and Discussion
Electron Microscopy
The particle sizes of the obtained samples were determined with a transmission electron microscope TEM 100-01.
Figure 1 displays TEM images of the obtained tin(II) oxalate samples. The figure shows that sample A has a wire-like form, while particles of sample B have an unspecified form and are more porous. These differences in morphology are caused by various pH of tin(II) oxalate precipitation. Presented appropriate selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns of the samples shows that the particles are polycrystalline.
Figures 2, 3, and 4 show high-resolution TEM images of the synthesized samples of SnO2, in which the individual crystal sizes are in the range of 40–200 nm. The TEM images also show that the particles of the SnO2 samples obtained from sample A are more agglomerated, characterized by smaller size (average size is 60–80 nm), and have are more uncertain form. While the particle size of the SnO2 samples obtained from sample B reached 200 nm. Powders represented as individual particles that have a pronounced hexagonal shape, which is especially distinct for sample 6. Thus, to obtain better crystals of tin(IV), oxide preferably used ammonium oxalate as a precursor of tin(II) oxalate.
Presented SAED patterns of the samples demonstrate single-crystalline spots. And, it will allow obtaining sensitive materials with high values of sensor response. Since the crystal quality does not seem to be good, the development of synthesis technique for improving the quality of the single crystals is therefore necessary.
X-ray Diffraction
XRD (X-ray diffraction) measurements were conducted using X-ray diffractometer Ultima IV Rigaku with CuКa radiation.
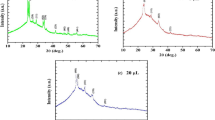
Figure 5 shows XRD spectra of the obtained samples of tin(II) oxalate which fit to the pure tin(II) oxalate (according card no. 01-072-9689, PDF-2/Release 2011 RD, ICDD). Diffraction patterns have different intensities of the main peaks. These differences are due to different morphology of samples A and B.
The average crystallite sizes of the obtained samples of SnC2O4 are 45.7 and 67.9 nm, respectively. The structural parameters (crystal grain size, lattice constants) of SnC2O4 samples presented in Table 3.
X-ray diffraction of the samples, which were obtained by decomposition of tin(II) oxalate at different temperatures, shows that pure SnO2 is formed in all cases besides powder obtained from sample A at temperature 850 K. Thus, 950 K is the minimum temperature for tin(IV) oxide synthesis from oxalate (Figs. 6, 7). Most distinct peaks on XRD patterns correspond to (110), (101) and (211) crystal faces (according card no. 1000062, USER (COD)). All diffraction lines can be indexed to the tetragonal rutile phase. For the samples, which were obtained from sample A the most distinct peak is (110), while for the samples, which were obtained from sample B, peak (101), that indicates the beginning growth of 1D nanostructures [21].
The comparison of the defined lattice constants for the samples with their standard values (a = 0.476, p = 0.318) shows that the crystalline lattice of SnO2 in samples was not deformed.
The structural parameters of SnO2 samples are presented in Table 4. According to the data presented in the table, with increasing temperature of heat treatment, the average crystallite size (and therefore particle size) increases. This is caused by the process of sintering particles.
Optical Spectra
Bandgap of SnO2 samples was determined by measuring the optical absorption of SnO2 films. Measurements were performed on a spectrophotometer UV-5800 PC.
Figure 8 shows dependences of the absorption coefficient on wavelength for samples 3 and 6. Limit wavelength values determined from the obtained diagrams are 328 and 336 nm for samples 3 and 6, respectively. The bandgap was calculated by the formula:

where h is the Planck constant and c is the speed of light.
The absorption coefficient α can also be expressed as:
where hν is the photon energy. Plots of (αhν) 2 versus hν can be derived from the absorption data in Fig. 8 as shown in the inset.
The values of the bandgap for samples 3 and 6 are different and equal to 3.78 and 3.69 eV, respectively These data show that the precursor affects not only the morphology of particles SnO2 samples, but also their electrical properties.
Conclusions
Characteristics of tin(IV) oxide highly depend on precursors used for the synthesis of tin(II) oxalate, which is confirmed by studies of electron microscopy, X-ray analysis, and optical spectra. The individual crystal sizes of synthesized SnO2 samples are in the range of 40–200 nm. The crystal lattice of SnO2 samples had shown no significant singular deformations. It is typical for the beginning growth of 1D nanostructures for the samples, which were obtained using tin chloride(II) and ammonium oxalate.
References
Zu Rong D, Zheng Wei P, Wang ZL (2003) Novel nanosturctures of functional oxides synthesized by thermal evaporation. Adv Funct Mater 13:9–24
Arafat MM, Dinan B, Sheikh A, Akbar SA, Haseeb ASMA (2012) Gas sensors based on one dimensional nanostructured metal-oxides: a review. Sensors 12:7207–7258
Yu-Feng S, Shao-Bo L, Fan-Li M, Jin-Yun L, Zhen J, Ling-Tao K, Jin-Huai L (2012) Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: a review. Sensors 12:2610–2631
Fine GF, Cavanagh LM, Ayo A, Russell B (2010) Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors 10:5469–5502
Jin H, Qing W (2009) Gas sensors based on semiconducting metal oxide one-dimensional nanostructures. Sensors 9:9903–9924
Miller TA, Bakrania SD, Perez C, Wooldridge MS (2006) Nanosturctured tin dioxide materials for gas sensor applications. Funct Nanomaterials 30:1–24
Matthias B (2006) Surface science studies of gas sensing materials: SnO2. Sensors 6:1345–1366
Chengxiang W, Longwei Y, Luyuan Z, Dong X, Rui G (2010) Metal oxide gas sensors: sensitivity and influencing factors. Sensors 10:2088–2106
Pan J, Shen H, Mathur S (2012) One dimensional SnO2 nanosructures: synthesis and application. J Nanotechnol 2012:12
A. Köck, A. Tischner, T. Maier, M. Kast, C. Edtmaier, C. Gspan, G. Kothleitner (2009) Atmospheric pressure fabrication of SnO2-nanowires for highly sensitive CO and CH4 detection. Sensors and Actuators B 138:160-167
Ji-Hye Park, Jong-Heun Lee (2009) Gas sensing characteristics of polycrastalline SnO2 nanowires prepared by polyol method. Sensors and Actuators B 136:151-157
Lu X, Yin L (2011) Porous indium oxide nanorods: synthesis, characterization and gas sensing properties. J Mater Sci Technol 27:680–684
Kim SS, Park JY, Choi S-W, Kim HS, Na HG, Yang JC, Kim HW (2010) Significant enhancement of the sensing characteristics of In2O3 nanowires by functionalization with Pt nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 21:415-–502
Lupan O, Chai G, Chow L (2008) Novel hydrogen gas sensor based on single ZnO nanorod. Microelectron Eng 85:2220–2225
Wan Q, Lin CL, Yu XB, Wang TH (2004) Room-temperature hydrogen storage characteristics of ZnO nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 84:124–126
Khanh LD, Bihn NT, Thanh LT, Long NN, Chi DH, Higashimine K, Mitani T (2008) SnO2 nanostructures synthesized by using a thermal evaporation method. J Korean Physi Soc 52(5):1689–1692
Castillo D. N., Becerril TD, Andres ER, Santiesteban HJ, Salgado GG (2012) VLS synthesis and characterization of SnO2 nanowires method. Mater Res Soc 1371:33-38
Zhihua Z, Jiang W, Handong L, Zhiming W (2012) Field emission from in situ-grown vertically aligned SnO2 nanowire arrays. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:117
Sitarz M, Kwoka M, Comini E, Zappa D, Szuber J (2014) Surface chemistry of SnO2 nanowires on Ag-catalyst-covered Si substrate studied using XPS and TDS methods. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):43
Ma J, Yingkai L, Heng Z, Ai P, Nailiang G, Ying Z (2014) Synthesis and high sensing properties of a single Pd-doped SnO2 nanoribbon. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):503
Choi Y-J, Hwang I-S, Park J-G, Kyoung Jin C, Jae-Hwan P, Jong-Heun L (2008) Novel fabrication of an SnO2 nanowire gas sensor with high sensitivity. Nanotechnology 19:4
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the faculty of physical engineering for their support in conducting this research.
Authors’ contributions
SN carried out the experimental studies, analysis and interpretation of data, drafted the manuscript. VL carried out the experimental studies and analysis and interpretation of data. TD carried out the coordination of experimental research, analysis and interpretation of data, drafted the manuscript. IA had given final approval of the version of the manuscript to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Nagirnyak, S.V., Lutz, V.A., Dontsova, T.A. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Tin(IV) Oxide Obtained by Chemical Vapor Deposition Method. Nanoscale Res Lett 11, 343 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1547-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1547-x