Abstract
Highly ordered TiO2 nanorod arrays (NRAs) were directly grown on an F:SnO2 (FTO) substrate without any seed layer by hydrothermal route. For a larger surface area, the second-step hydrothermal treatment in hydrochloric acid was carried out to the as-prepared TiO2 NRAs. The results showed that the center portion of the TiO2 nanorods were dissolved in the etching solution to form a nanocave at the initial etching process. As the etching time extended, the tip parts of the nanocave wall split into lots of nanowires with a reduced diameter, giving rise to a remarkable increase of specific surface area for the TiO2 NRAs. The TiO2 films after etching treatment were sensitized by CdS quantum dots (QDs) to fabricate quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs), which exhibited a significant improvement in the photocurrent density in comparison with that of the un-treated device, this mainly attributed to the enhancement of QD loading and diffused reflectance ability. Through modifying the etching TiO2 films with TiCl4, a relatively high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 3.14 % was obtained after optimizing the etching time.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Recently, quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs) have attracted much interesting research attributed to their unique advantages involving low cost and high theoretical conversion efficiency [1–3]. In typical configuration of QDSSCs, inorganic semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) such as CdS [4–6], CdSe [7, 8], CdTe [9, 10], and PbS [11] were usually used as sensitizer and exhibited huge advantages over organic dyes, such as low cost, high molar extinction coefficient, size-dependent band gap, and multi-exciton generation effect [12–14]. In addition, TiO2 semiconductor as the most successful photoanode material was served as a scaffold layer to adsorb QDs and a medium layer to transport a photo-generated electron. Therefore, the specific surface area and the electron mobility of TiO2 photoanode play a key role on the photovoltaic performance of QDSSCs. The electron mobility is defined as the drift velocity of electrons under the driving force of an extra electrical field. Hendry et al. had demonstrated that electron mobility is strongly dependent on the material morphology in nanostructured polar materials due to local field effects [15]. In order to speed up the electron mobility and decrease the possibility of photo-generated charge recombination, 1D nanostructures such as nanotubes [16], nanorods [17, 18], and nanowires [19] were utilized as photoanode for QDSSCs, which supplied direct electrical pathways and facilitate electron transportation; this was considered as a powerful strategy to reduce the electron–hole recombination which abundantly existed in TiO2 nanoparticle-based solar cell. Among these 1D architectures, researchers had paid much attention to the rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays (NRAs) due to their superior electrical transport performance, excellent chemical stability, high refraction index, and cheap product cost [20–22]. However, it has a vital shortcoming, i.e., small surface area which results in poor QD loading. Thus, the QDSSCs fabricated from the rutile TiO2 NRAs exhibited poor photovoltaic performance. A lot of methods have been reported for enlarging the specific surface area of the rutile TiO2 NRAs. For example, Lv et al. developed a feasible etching treatment to TiO2 NRAs in hydrochloric acid solution under hydrothermal condition, which induced the compact TiO2 nanorods split into lots of small nanowires; thus, this method significantly improves the surface area of the TiO2 films and in turn, allowed superior dye-loading capacity of the TiO2 photoanode, a highest power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 7.91 % was achieved from the DSSCs assembled by the etching TiO2 films [23, 24]. From that on, the etching treatment was considered as a powerful strategy for enlarging the inner surface area of the TiO2 NRAs. Yuan et al. synthesized long single-crystalline rutile TiO2 NRAs with a high surface area by combining a mild hydrothermal method with a chemical etching route, and the DSSCs constructed by 7-h-etched TiO2 NRAs exhibited a PCE of 4.69 % [25]. Chen’s group fabricated an ultralong TiO2 NRAs (17.6 μm) with a large inner surface area by using a hydrothermal method and post-etched with hydrochloric acid at high temperature. Such TiO2 NRAs were utilized as photoanode for CdS/CdSe co-sensitized solar cells and reached a maximum value of 17.22 mA/cm2, yielding the highest PCE of 2.66 % [26]. Huang et al. grown polycrystalline TiO2 NRAs on FTO substrate and in situ converted NRAs into nanotube arrays (NTAs) by hydrothermal etching. After conversion, more CdSe QDs can be filled in the NTAs, so the PCE of QDSSCs increases by 60 %. QDSSCs with half-etched TiO2 nanotubes achieved the best conversion efficiency of 2.44 % [27].
In our work, the moderate etching treatment was introduced to short TiO2 NRAs (3.6 μm) and the CdS QDs prepared by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) was used as the single sensitizer. We focused on the effect of etching time toward QDSSC performance and the underlying reason. Through optimizing the etching time, a PCE of 3.14 % was obtained after TiCl4 modifying under the illumination of 100 mW/cm2 AM 1.5G solar simulators, this is a relative good performance for CdS-sensitized TiO2 NRAs solar cells.
Methods
Hydrothermal Synthesis of TiO2 NRAs
Hydrothermal synthesis reported by Liu and Aydil was employed for the growth of highly aligned rutile TiO2 NRAs [28]. In a typical synthesis, 8 ml deionized water (DI) and 8 ml hydrochloric acid (HCl) with 36.5–38 wt% concentration were mixed together and stirred for 5 min to achieve a homogeneous solution, then 220 μl of titanium butoxide were added into this solution as titanium precursor, followed by another stir until the titanium butoxide was completely dissolved in the hydrochloric acid solution. Finally, the resultant solution was poured into a Teflon-lined container sealed by a stainless steel autoclave (25-ml volume). A piece of FTO glass with a size of 2 cm × 2 cm was used as substrate and leaned on the wall of the reactor with an angle and the conductive side of the FTO substrate faced down. The reactor was transferred into an oven with a temperature at 150 °C maintained for 10 h. While waiting for hydrothermal synthesis to finish and the reactor to cool down to room temperature, the FTO substrate grown by TiO2 NRAs was taken out, carefully washed by DI water, and dried using N2 gas flow. Finally, the resultant TiO2 films were suffered from an annealing at 500 °C for 2 h under air condition.
Etching Treatment to the TiO2 NRAs
Seven milliliters of deionized water was mixed with 9 ml HCl to form an etching solution, then the mixture was transferred into a Teflon-lined container and the TiO2 NRAs synthesized by a hydrothermal method were immersed in the etching solution, and the Teflon-lined container was sealed by a stainless steel autoclave. The hydrothermal etching treatment was conducted at 150 °C for 4–6 h. After the autoclave cooled down, the TiO2 films on the FTO substrate was taken out from the reactor and immersed in DI water for 2 h to remove the residual acid.
TiCl4 Treatment to the Etching TiO2 Films
The etching TiO2 films were further modified by TiCl4 aqueous solution. In the typical treatment process, the etched TiO2 films were immersed in 0.3 M TiCl4 aqueous solution at 70 °C for 30 min. After modification, the samples were extensively rinsed with absolute ethanol and followed by 500 °C annealing treatment for 1 h in air.
Deposition CdS QDs onto TiO2 Photoanode
The SILAR method was used for the preparation of CdS QDs on TiO2 films. Briefly, the TiO2 films treated by hydrochloric acid and TiCl4 were immersed in an aqueous solution of Cd(OOCH3)2 (0.3 M) for 2 min and rinsed with DI water, then immersed in 0.3 M Na2S aqueous solution for another 2 min, followed by another rinsing with DI water. Such a SILAR cycle was repeated several times to obtained the desired thickness of the CdS layer. The TiO2/CdS photoelectrodes were sintered at 380 °C for 1 h to improve the crystallinity of the CdS QDs
Characterization
The field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, JEOL JSM-7100F) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEOL JEM 2010) were used for the morphological observation of the samples. The crystalline structure of the products was characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Brucker D8), the XRD patterns were collected from the samples grown on FTO substrates via θ–2θ scanning mode, and Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54060 Å) was used as the source operating at 45 kV and 40 mA. The light absorption and the diffused reflectance spectra were examined by UV-vis spectrophotometer (UV-3600, Shimadzu). The Pt films sputtered on an FTO glass substrate was served as the counter electrode and face to face bonded with the TiO2/CdS photoelectrode. Polysulfide electrolyte was applied as redox couples and injected into the free space between the two electrodes to complete the QDSSC fabrication. The photocurrent density versus voltage (J–V) curves of the cells were recorded by digital multi-meter (Keithley 2402) under the illumination of an AM 1.5G solar simulator (Newport, 100 mW/cm2), and the irradiated area of devices was defined to be 0.125 cm2 using a mask.
Results and Discussion
Figure 1 presents the detailed SEM images of as-prepared TiO2 NRAs and the nanorods etched for different times. It is obviously seen from Fig. 1a that TiO2 nanorods were uniformly distributed on the entire surface of the FTO glass substrate after 10-h hydrothermal synthesis. The nanorods display a geometric shape of tetragonal pillar, which agrees well with the growth preference of tetragonal crystal structure for TiO2 nanorod hydrothermal synthesis. The inset in Fig. 1a reveals the detailed top facet of the individual nanorod, lots of step edges can be observed on the top facet of the nanorods, which result from the different growth rates at axial direction among various spots of one nanorod, such step edges provide further substrate for the next growth of the nanorods, whereas the profile of the nanorods display smoothness. Moreover, these nanorods exhibited a large mean diameter about 150 nm, and some adjacent nanorods contacted each other; little space existed among the contacted nanorods, such structure prevented electrolyte to penetrate in and was adverse for solar cell application. So, etching treatment is indispensable for improving the gap space. The as-prepared TiO2 NRAs were immersed in a mixed solution that contained 7 ml DI water and 9 ml HCl and suffered from the hydrothermal etching for different times. Figure 1b–d exhibits the morphological character of the TiO2 NRAs etched for various times. When etched for 4 h, the center portion of the TiO2 nanorods were cut off by the HCl solution, and the nanorods had transformed into a nanocave, which presented an average inner diameter of 120 nm and a wall thickness of 10 nm. The reaction happened in the etching processes could be expressed by the following formula [26, 27].
As the formula expressed, the reaction is reversible, and there are two competing reactions in this system. On the one hand, the TiO2 was dissolved in hydrochloric acid solution to produce the Ti (IV) complex. On the other hand, the Ti (IV) complex will hydrolyze into TiO2. However, during the etching treatment, the etching solution, contained 9 ml HCl and 7 ml DI water, will push the reaction along the dissolved direction. In addition, the surface stability and reactivity of the TiO2 nanorods are dominated by surface chemistry, which is critical for the equilibrium morphology [29]. The surface energy of the rutile TiO2 nanorods follows sequences (110) < (100) < (101) < (001) [30, 31]. Generally, the facet with higher surface energy diminishes faster for minimization of the total surface energy. The (001) face corresponds to the core of the TiO2 nanorods, and the (110) face is the sidewall of the TiO2 nanorods. Thus, the (001) core of the TiO2 nanorods is etching faster than the (110) face of the sidewall. As a result, nanocaves appeared on the center portion of the TiO2 nanorods by hydrothermal selective etching of the core and the remaining sidewall of (110) face, which can be obviously detected from the inset of Fig. 1b. For the 5-h-etched sample, the inner diameter of the TiO2 nanocave continually enlarged. Interestingly, it can be found that the tip wall of the nanocave was divided into lots of small nanowires, and the amount and length of secondary nanowires increased as the etching time extended to 6 h. In order to better understand the etching treatment, the schematic diagrams of the etching process was presented in Additional file 1: Figure S1, images (a), (b), (c), and (d) correspond to the structure of the TiO2 films etching for 0, 4, 5, and 6 h, respectively. The inset defines the depth and the inner diameter of the nanocaves. As the Additional file 1: Figure S1 depicted, when the etching time was 4 h, the center portion of the nanorods was cut off by hydrochloric acid to form a nanocave. As the etching time was prolonged to 5 h, the upper part of the nanocave wall would split into small nanowires. Extending the etching time, the length and the amount of the secondary nanowires were continually increased.
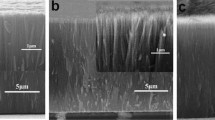
Figure 2a, b reveals the cross-sectional views of the TiO2 NRAs before and after the 6-h etching treatment. For the as-prepared sample, the thickness of the nanorod films was 3.6 μm, and the nanorods display high density; there is a little space between the adjacent nanorods especially for the bottom part of the arrays, which is well consistent with the result of Fig. 1a. As shown in Fig. 2b, the NRAs after 6-h etching exhibited almost the identical thickness with the original sample. Furthermore, the hydrothermal etching lead the virgin TiO2 nanorod to split into lots of small nanowires, and the compact NRAs became loose. Thus, the interstitial space between the adjacent nanorods dramatically amplified especially for the upper half part of the TiO2 NRAs, resulting in a large surface area for the TiO2 NRAs. The further detailed morphology of the 6-h etching samples was detected by TEM. From Fig. 2c, d, it can be obviously seen that the tip part of the nanorod was divided into lots of small nanowire with a diameter of 20 nm. The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern revealed that the nanorods was single-crystal TiO2, and such structure displays unique advantage in QDSSC application, because they can provide high-speed pathway for electron transport with few crystal boundary.
Figure 3 shows the top views of the TiO2 films sensitized by CdS QDs. It can be seen from Fig. 3a that a plentiful of CdS nanoparticles were covered on the surface of the as-prepared TiO2 nanorods to form TiO2/CdS nanocable. In addition, the side and top faces of the nanorods were roughened by CdS nanocrystal, which may be in favor of the incident light absorption and diffused reflection. The worth noting point was that the TiO2/CdS nanocable became very compact after CdS coating, a little free space was left in the films, it would prevent the electrolyte to penetrate into and blocked the CdS sensitizer contact with electrolyte, and this was adverse for the PCE of the assembled QDSSCs. For the 4-h etching sample, the inner and outer surfaces of the nanocave were attached by CdS QDs, and the amount of QDs was obviously greater than that of un-etching sample. Moreover, it can be found that the gap space between the adjacent nanocables became large, which was in favor of QDSSC utilization. When etching duration prolonged to 5 h, the wall of the nanocaves was further split into lots of small nanowires, and all surfaces of the small nanowires can provide sites for CdS QD adsorption, which results in the enhancement of QD loading. In addition, the amount of QDs deposited on the TiO2 films further increased when the etching time extended to 6 h, because the length and the amount of the secondary nanowires continually increased as shown in Fig. 1d. The typical TEM images of CdS-sensitized 6-h-etched TiO2 NRAs have been provided in Fig. 3e, f. From the images, we can see that the CdS sensitizers sufficiently cover the secondary nanowires, the CdS nanoparticles are faceted with occasionally irregular shapes, and the particles presents a size ranges from 5 to 15 nm.
The microstructure of the TiO2 NRAs before and after the etching treatment are presented in Fig. 4a, b characterized by an XRD instrument. For the FTO/TiO2 un-treated sample, except for the peaks from the FTO substrate, the diffraction peaks located at 36.2° and 62.8° can be indexed to the (101) and (002) planes of tetragonal rutile TiO2 (PCPDF No.89-4920), and the (101) peak exhibited the strongest intensity. The similar result had also been detected in other literatures [32–34]. For the rutile TiO2 powder containing randomly oriented crystals, the most intense diffraction peak should be the (110) (the reference data in JCPDS 89-4920) which was similarly observed for the rod-shaped rutile TiO2 nanoparticles [35]. However, in our case, the (101) peak presents the highest diffraction intensity, whereas the (110) peak intensity is noticeably weak. The highly intense (101) peak along with the enhanced (002) peak in the NRA film indicates that the rutile crystal grows with (101) plane parallel to the FTO substrate and the nanorods are oriented along the [002] direction. Comparing the XRD patterns of the TiO2 films before and after the etching treatment, we can found that both of the two samples exhibited the identical diffraction peaks position regardless of the intensity difference, demonstrating that the etching treatment in hydrochloric acid have not damaged the rutile crystal structure of the TiO2 films. The rutile TiO2 exhibits some advantages over anatase such as higher chemical stability, higher refractive index, and cheaper production cost. Besides these advantages, TiO2 NRAs with rutile phase has approximately 100 times larger electron mobility than nanoparticles TiO2, which results from its one-dimensional structure, highly crystalline and defect-free. Thus, the TiO2 NRAs with a rutile phase exhibits unique superiority in the application of sensitized solar cell due to its lower electrical transport resistance, and this was in favor of reducing the electron recombination rate [15, 17, 36]. The XRD patterns of FTO/TiO2/CdS are shown in Fig. 4c, and besides the peaks indexed to SnO2 and TiO2, the other three peaks appeared at 25.1°, 28.4°, and 43.9° which matched well with the (100), (101), and (110) planes of hexagonal CdS (JCPDS no. 06-0314), respectively. Moreover, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the CdS diffraction peaks are broad, suggesting the small particle size of CdS QDs deduced by Debye–Scherrer equation.
Figure 5a gives the Uv-vis absorption curves of the TiO2 films before and after hydrothermal etching. For the un-etching sample, a steep UV absorption edge occurs at ~410 nm, and TiO2 displays no absorption in the visible light range due to its large band gap of 3.2 eV. Comparing the light absorption curves before and after the etching treatment, it can be found that the two samples exhibited the same absorption edge, because the etching treatment does not change the rutile crystal structure of TiO2 nanorod as the XRD result shown. In addition, the light-scattering capacity of the photoanode has significant influence on the light-harvesting performance of the photoelectrode (photoanode sensitized by QDs). When the incident light irradiates on the photoelectrode, the photoanode with superior light-reflectance ability should has a high probability for capturing the incident light, this can helps to improve the short-circuit current density (J sc). Usually, the light-scattering ability can be characterized by diffused reflectance spectra. Figure 5b shows the diffused reflectance spectra of the un-treated and 5-h etching TiO2 films, and it can be found that the reflectance index of the etching sample was higher than that of the un-etching sample; this can be explained by the relatively random structure after the etching treatment, such random structure can provide more light-scatter points [37, 38].
Figure 6 reveals the typical optical absorbance spectra of the TiO2/CdS photoelectrodes with different etching time. In comparison with the pure TiO2 photoanode, the light absorbance of TiO2/CdS photoelectrodes exhibited significant enhancement in visible light region, suggesting that the CdS QD was an efficient photo-sensitizer for QDSSC utilization. Moreover, the additional absorption edge emerged at 525 nm for TiO2/CdS photoelectrodes corresponding to the CdS band gap of 2.36 eV. In addition, it can be found that the absorbance intensity in visible light region enhanced with the etching duration, this may be due to the increase of CdS nanoparticles amount attached on the TiO2 photoanode surface as shown in Fig. 3.
The TiO2/CdS photoelectrodes with different etching times were face to face bonded with FTO/Pt counter electrodes to assemble QDSSCs, and the sulfide-based electrolyte was used as redox couples to maintain the photo-sensitizer electrical neutrality. Figure 7 shows the dark J–V curves of QDSSCs constructed from the TiO2 films with different etching times. All the curves indicated typical rectifying behavior as the diode property. When the extra voltage was applied between the photoelectrode and counter electrode, the intrinsic electron in the CdS QDs would transport along a certain direction under the force of electrical field, which caused the dark current. The magnitude of the dark current can be used to estimate the charge recombination [39]. In general, the electron recombination reaction involved two processes: the photoinjected electrons in TiO2 conduction band recombined with the oxidized QDs and/or with Sx 2− in the electrolyte. Because the regeneration of the QDs by S2− is remarkably faster than the charge transfer from TiO2 to the oxidized QDs, the recombination between photo-generated electron and the oxidized QDs is negligible. Thus, the dark current usually represented the recombination between Sx 2− ions and the photo-generated electrons in the semiconductor [40]. The etching photoanode displays a higher dark current compared with the un-etching samples, indicating more charge recombination in the etching samples, and this may be attributed to the enhancement of electron trapping sites after etching treatment.
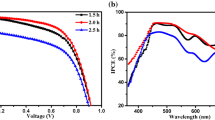
Figure 8 presents the photocurrent density-voltage performance of QDSSCs made from TiO2/CdS photoelectrodes with various etching times. The detail photovoltaic parameter of the QDSSCs including short-circuit current density (J sc), open-circuit voltage (V oc), fill factor (FF), and power conversion efficiency (η), are listed in Table 1. As shown in Table 1, the cell constructed by un-treated TiO2 NRAs gives a J sc of 1.96 mA/cm2, an V oc of 0.45 V, and a FF of 42.9 %, yielding a η of 0.38 %. Through the etching treatment, the cells exhibit remarkable increase in J sc and V oc compared with that of the un-treated sample, and these results are mainly contributed by the enhanced QD loading ability, which ascribes to the enlarged surface area after hydrothermal etching. In addition, the PCE initially increases with etching time then decreases. A maximum PCE of 1.07 % is obtained when the etching time is 5 h. As the SEM analysis, the amount of QD loading increased with the etching duration, which helps to strengthen the visible light absorption. Therefore, the photo-generate current density increases when the etching time increases from 4 to 5 h, yielding an improvement in PCE. As the etching time continually extended to 6 h, the interface between TiO2 nanorods and FTO substrate will become unstable after long-term corrosion, because the TiO2 nanoparticle in the interfaces will gradually dissolve in acid solution, and the interface resistance increases, which results in the decrease of the PCE afterwards.
The titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) treatment is considered as an effective route for improving the photovoltaic properties of QDSSCs. In this work, the TiCl4 modification was carried out to the TiO2 films with different etching times. As the typical modification process, the TiO2 films etched for various times were immersed in 0.3 M TiCl4 aqueous solution at 70 °C for 30 min. After the treatment, the samples were taken out from the TiCl4 aqueous solution, extensively rinsed with absolute ethanol, and then annealed at 500 °C in air atmosphere for 1 h. Additional file 1: Figure S2 shows the SEM image of the TiO2 NRAs modified with 0.3 M TiCl4 at 70 °C for 30 min. It can be observed that the side face of the NRAs was attached with lots of TiO2 nanoparticles after TiCl4 treatment, which roughened the surface, and the size of the nanoparticle was 2 nm. Figure 9 reveals the J–V curves of the QDSSCs assembled by the TiO2 photoanode treated with TiCl4 under the illumination of AM 1.5 solar simulators (100 mW/cm2), and the corresponding parameters of photovoltaic performance are deduced and summarized in Table 2. As shown in Table 2, the cell fabricated from the un-etching TiO2 NRAs treated with TiCl4 gives a J sc of 2.33 mA/cm2, an V oc of 0.61 V, a FF of 41.4 %, and a η of 0.59 %. In addition, it is worth noting that the TiCl4 treatment gives rise to the higher J sc values than that of the un-treating sample. A highest PCE of 3.14 % is achieved after TiCl4 treatment. As the SEM in Additional file 1: Figure S2 shown, after TiCl4 modification, a lot of extra TiO2 nanoparticles were synthesized on the surface of the prepared TiO2 nanostructure, which lead to the further increase of TiO2 specific surface area. Consequently, the QD loading ability of the photoanode was strengthened. Moreover, a thin TiO2 layer was covered on the bare surface of FTO substrate after TiCl4 modification, which can block the recombination between electrons in photoanode and positive charge in electrolyte [41, 42]. In addition, TiCl4 modification can also improve the light-scattering capacity of the TiO2 films. All these functions of TiCl4 treatment resulted in high energy conversion.
Conclusions
In this study, a hydrothermal method was used to grow TiO2 NRAs on FTO substrate. For the sake of a large specific surface area, a facile hydrothermal etching was employed to the TiO2 NRAs. The relation between the etching time and the performance of TiO2 films had been comprehensively studied. The results showed that the etching treatment enlarged the gap space among the compact nanorods and hollowed out the center part of the nanorod to form a nanocave, and the wall of the nanocave split into lots of small nanowires; these changes in morphology lead to the improvement of the surface area. In addition, the hydrothermal etching in HCl solution did not damage the rutile crystal structure of the TiO2 nanorods and enhanced the diffused reflectance ability of photoanode. All these factors resulted in better photovoltaic performance for the QDSSCs made from the etching TiO2 films. Finally, through modifying with TiCl4, a relatively high PCE of 3.14 % is obtained after optimizing the etching time.
References
Rühle S, Shalom M, Zaban A (2010) Quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. ChemPhysChem 11:2290–2304
Zhang YH, Zhu J, Yu XC, Wei JF, Hu LH, Dai SY (2012) The optical and electrochemical properties of CdS/CdSe co-sensitized TiO2 solar cells prepared by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction processes. Solar Energy 86:964–971
Wu YA, Warner JH (2012) Shape and property control of Mn doped ZnSe quantum dots: from branched to spherical. J Mater Chem 22:417–424
Lee W, Min SK, Dhas V, Ogale SB, Han SH (2009) Chemical bath deposition of CdS quantum dots on vertically aligned ZnO nanorods for quantum dots-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem Commun 11:103–106
Chang CH, Lee YL (2007) Chemical bath deposition of CdS quantum dots onto mesoscopic TiO2 films for application in quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 91:053503–053506
Shen YJ, Lee YL (2008) Assembly of CdS quantum dots onto mesoscopic TiO2 films for quantum dot-sensitized solar cell applications. Nanotechnology 19:045602
Diguna LJ, Shen Q, Kobayashi J, Toyoda T (2007) High efficiency of CdSe quantum-dot-sensitized TiO2 inverse opal solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 91:3116
Lee H, Wang M, Chen P, Gamelin DR, Zakeeruddin SM, Gratzel M, Nazeeruddin MK (2009) Efficient CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells prepared by an improved successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction process. Nano Lett 9:4221–4227
Lan GY, Yang Z, Lin YW, Lin ZH, Liao HY, Chang HT (2009) A simple strategy for improving the energy conversion of multilayered CdTe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem 19:2349–2355
Wang XN, Liu R, Wang T, Wang BY, Xu Y, Wang H (2013) Dual roles of ZnS thin layers in significant photocurrent enhancement of ZnO/CdTe nanocable arrays photoanode. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:3312–3316
Wang XH, Koleilat GI, Tang J, Liu H, Kramer IJ, Debnath R, Brzozowski L, Barkhouse DAR, Levina L, Hoogland S, Sargent EH (2011) Tandem colloidal quantum dot solar cells employing a graded recombination layer. Nat Photonics 5:480–484
Yu WW, Qu LH, Guo WZ, Peng XG (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854–2860
Ekimov AI, Efros AL, Onushchenko AA (1985) Quantum size effect in semiconductor microcrystals. Solid State Commun 56:921–924
Takagahara T, Takeda K (1992) Theory of the quantum confinement effect on excitons in quantum dots of indirect-gap materials. Phys Rev B 46:15578
Hendry E, Koeberg M, Regan BO, Bonn M (2006) Local field effects on electron transport in nanostructured TiO2 revealed by terahertz spectroscopy. Nano Lett 6:755–759
Sun WT, Yu Y, Pan HY, Gao XF, Chen Q, Peng LM (2008) CdS quantum dots sensitized TiO2 nanotube-array photoelectrodes. J Am Chem Soc 130:1124–1125
Bang JH, Kamat PV (2010) Solar cells by design: photoelectrochemistry of TiO2 nanorod arrays decorated with CdSe. Adv Funct Mater 20:1970–1976
Hu YX, Wang BY, Zhang JQ, Wang T, Liu R, Zhang J, Wang XN, Wang H (2013) Synthesis and photoelectrochemical response of CdS quantum dot-sensitized TiO2 nanorod array photoelectrodes. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:222
Baxter JB, Aydil ES (2005) Nanowire-based dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl Phys Lett 86:053114
Wang BY, Ding H, Hu YX, Zhou H, Wang SQ, Wang T, Liu R, Zhang J, Wang XN, Wang H (2013) Power conversion efficiency enhancement of various size CdS quantum dots and dye co-sensitized solar cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38:16733–16739
Hu HW, Ding JN, Zhang S, Li Y, Bai L, Yuan NY (2013) Photodeposition of Ag2S on TiO2 nanorod arrays for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:10
Wang BY, Liu T, Xia C, Zhou FY, He F, Liu R, Hu YX, Wang H (2014) The structure and photovoltaic properties of double-shell TiO2/ZnSe/CdSe nanocable arrays synthesized by using TiO2/ZnO nanocables template. Mater Res Bull 59:234–240
Lv MQ, Zheng DJ, Ye MD, Sun L, Xiao J, Guo W, Lin CJ (2012) Densely aligned rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays with high surface area for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 4:5872–5879
Lv MQ, Zheng DJ, Ye MD, Xiao J, Guo WX, Lai YK, Sun L, Lin CJ, Zuo J (2013) Optimized porous rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays for enhancing the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ Sci 6:1615–1622
Yuan T, Lu HB, Dong BH, Zhao L, Wan L, Wang SM, Xu ZX (2015) Single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays with high surface area for enhanced conversion efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26:1332–1337
Chen C, Ye MD, Lv MQ, Gong C, Guo WX, Lin CJ (2014) Ultralong rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays with large surface area for CdS/CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 121:174–182
Huang H, Pan L, Lim CK, Gong H, Guo J, Tse MS, Tan OK (2013) Hydrothermal growth of TiO2 nanorod arrays and in site conversion to nanotube arrays for highly efficient quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Small 18:3153–3160
Liu B, Aydil ES (2009) Growth of oriented single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorods on transparent conducting substrates for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 131:3985–3990
Yang HG, Sun CH, Qiao SZ, Zou J, Liu G, Smith SC, Cheng HM, Lu GQ (2008) Anatase TiO2 single crystals with a large percentage of reactive facets. Nature 453:638–641.
Kumar A, Madaria AR, Zhou CW (2010) Growth of aligned single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanowires on arbitrary substrates and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem C 114:7787–7792
Cheng HM, Ma JM, Zhao ZG, Qi LM (1995) Hydrothermal preparation of uniform nanosize rutile and anatase particles. Chem Mater 7:663–671
Li YT, Wei L, Chen XY, Zhang RZ, Sui X, Chen YX, Jiao J, Mei LM (2012) Efficient PbS/CdS co-sensitized solar cells based on TiO2 nanorod arrays. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:67
Xie YR, Wei L, Wei GD, Li QH, Wang D, Chen YX, Yan SS, Liu GL, Mei LM, Jiao J (2013) A self-powered UV photodetector based on TiO2 nanorod arrays. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:188
Kim HS, Lee JW, Yantara N, Boix PP, Kulkarni SA, Mhaisalkar S, Grӓtzel M, Park NG (2013) High efficiency solid-state sensitized solar cell-based on submicrometer rutile TiO2 nanorod and CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite sensitizer. Nano Lett 13:2412–2417
Park NG, Schlichthӧrl G, Lagemaat JVD, Cheong HM, Mascarenhas A, Frank AJ (1999) Dye-sensitized TiO2 solar cells: structural and photoelectrochemical characterization of nanocrystalline electrodes formed from the hydrolysis TiCl4. J Phys Chem B 103:3308–3314
Feng XJ, Zhu K, Frank AJ, Grimes CA, Mallouk TE (2012) Rapid charge transport in dye-sensitized solar cells made from vertically aligned single-crystal rutile TiO2 nanowires. Angewandte Chemie 124:2781–2784
Liu L, Qian JS, Li B, Cui YM, Zhou XF, Guo XF, Ding WP (2010) Fabrication of rutile TiO2 tapered nanotubes with rectangular cross-sections via anisotropic corrosion route. Chem Commun 46:2402–2404
Pan H, Qian JS, Yu A, Xu MG, Tu L, Chai QL, Zhou XF (2011) TiO2 wedgy nanotubes array films for photovoltaic enhancement. Appl Surf Sci 257:5059–5063
Zhang QX, Guo XZ, Huang XM, Huang SQ, Li DM, Luo YH, Shen Q, Toyada T, Meng QB (2011) Highly efficient CdS/CdSe-sensitized solar cells controlled by the structural properties of compact porous TiO2 photoelectrodes. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 13:4659–4667.
Lee WJ, Lee JW, Lee SJ, Yi WK, Han SH, Cho BW (2008) Enhanced charge collection and reduced recombination of CdS/TiO2 quantum-dots sensitized solar cells in the presence of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 92:153510
Yu H, Pan J, Bai Y, Zong X, Li XY, Wang LZ (2013) Hydrothermal synthesis of a crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorod based network for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem A Eur J 19:13569–13574
Wang HE, Chen ZH, Leung YH, Luan CY, Liu CP, Tang YB, Yan C, Zhang WJ, Zapien JA, Bello I, Lee ST (2010) Hydrothermal synthesis of ordered single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays on different substrates. Appl Phys Lett 96:263104
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51372075, 51502084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ Contributions
JW prepared the TiO2 photoanode and constructed the QDSSCs, also drafted the manuscript. RL analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. YT and SC carried out the material characterization. YH measured the photovoltaic performance of the devices. BW contributed to the design of the experiment and analysis of the data. YX participated in the discussion of data analysis and give some useful advices. HW supervised the work, commented and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Jingshu Wan and Rong Liu contributed equally to this work.
Additional file
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
The schematic diagrams of the etching process. Images (a), (b), (c), and (d) correspond to the structure of TiO2 films etching for 0, 4, 5, and 6 h. The inset defines the depth and the inner diameter of the caves. Figure S2. The SEM images of the TiO2 NRAs modified with 0.3 M TiCl4 at 70 oC for 30 min.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, J., Liu, R., Tong, Y. et al. Hydrothermal Etching Treatment to Rutile TiO2 Nanorod Arrays for Improving the Efficiency of CdS-Sensitized TiO2 Solar Cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 11, 12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1236-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1236-9