Abstract
NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:x%Er3+ (x = 0, 6, 8, 10, and 12) active-core/active-shell nanoparticles (NPs) were peculiarly synthesized via a delayed nucleation pathway with procedures. The phase, shape, and size of the resulting core–shell NPs are confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Coated with a NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active shell around the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core NPs, a maximum luminescent enhancement of about 336 times higher than the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core-only NPs was observed under the 1540 nm excitation. The intensity ratio of green to red was adjusted through the construction of the core–shell structure and the change of Er3+ concentration in the shell. By analyzing the lifetimes of emission bands and exploring the energy transition mechanism, the giant luminescence enhancement is mainly attributed to the significant increase in the near-infrared absorption at 1540 nm and efficient energy migration from the shell to core.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Upconversion (UC) refers to nonlinear optical processes characterized by the successive absorption of two or more pump photons via intermediate long-lived energy states, followed by the emission of the output radiation at a shorter wavelength than the pump one [1]. With the rapid development of nanotechnology, a large amount of high-quality lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) were synthesized and have been applied in various fields, such as solar cells [2, 3], bioimaging [4, 5], photo-catalysis [6], three-dimensional displays [7], and flash memories [8]. Especially for crystalline silicon solar cells, the adoption of UCNPs was proved to greatly improve the utilization of the solar energy. Nevertheless, the part (which wavelength is longer than 1100 nm) of solar energy will be lost for that the Si semiconductor cannot absorb the energy below its band gap (1.12 eV). And the propositon of UCNPs under the excitation of 1540 nm is an excellent way to reduce these sub band gap transmission losses. Thus, it becomes an important topic to utilize this part of solar energy more efficiently.
Moreover, the major challenge for UCNPs is still how to gain stronger upconversion luminescence with more optimized structures and synthesis methods. To overcome this challenge, many efforts were made, including changing the composition, tuning the morphology and size, and surface modification [9–17]. Among these methods, constructing core/shell architecture is thought to be the commonest but one of the most effective routes to improve the efficiency of UCNPs. By growing a shell around the luminescent core with similar lattice parameters, the lanthanide ions in the core were mostly protected from non-radiative decay caused by the surface defects. Besides, it is not until recent years that an active core/active shell structure is developed [9, 18–28]. Compared with traditional core/shell structure with an inert shell, an active shell not only protects the core from surface defects but also transfers absorbed near infrared (NIR) light from the pump source to the core NPs. In other words, the active shell acts as a sensitizer for the Ln3+-doped active core to increase the intensity of UC.
Commonly, an emissive UCNP consists of an inert host matrix and active Ln3+ ions as luminescent centers [29]. As an ideal activator, the ion tends to possess the ability of extracting energy from nearby excited sensitizers to promote further transitions to higher energy levels. Besides, to confine the process of non-radiative relaxations, the activator is likely to have energy levels separated to each other properly. According to the considerations above, Er3+, Tm3+, and Ho3+ are thought to be desired candidates. Moreover, Er3+ turns out to be the most effective one during the UC process, owing to its similar energy gaps. But, if simply increasing the concentration of Er3+ in the NPs, the luminescence shows a nonlinear relationship with the concentration of Er3+ and sometimes the luminescence intensity even decrease with the augment of Er3+, due to the influence of energy migration and concentration-quenching effects at higher concentrations.
Except successful construction of the active-core/active-shell structure, a strategy to improve the intensity of upconversion luminescence by only Er3+ ion-doped NaGdF4 was developed in this work. Compared to the inert shell, the UC luminescence was largely enhanced by adopting the method of the active shell and optimizing the Er3+ concentration. The luminescence properties of novel NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4: 10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell NPs (Er3+ doping in mol% relative to Gd) were also discussed in detail under the 1540-nm excitation.
Methods
Materials
The starting materials were sodium trifluoroacetate (CF3COONa; reagent grade, 99%), trifluoroacetic acid (CF3COOH; reagent grade, 99%), gallium oxide (Gd2O3, 99.99%), and europium oxide (Er2O3, 99.99%). Cyclohexane (analytical grade, 99.5%), oleic acid (OA; analytical grade), oleylamine (OM; 80–90%), and absolute ethanol were used. Deionized water was used throughout. All chemical materials were used as received without further purification.
Preparation of NaGdF4:12%Er3+ NPs
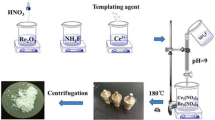
At the beginning, rare earth (RE) trifluoroacetate (RE(CF3COO)3; RE = Gd, Er) precursor was prepared as follows: rare earth oxides were dissolved in trifluoroacetic acid (CF3COOH) with certain amount of deionized water until the solution was transparent. The solution was then filtered, followed by drying at 140 °C for dozens of hours. The synthesis basically followed the routes previously reported in literature [30]. A mixture of a designated molar ratio of CF3COONa (1 mmol), Gd(CF3COO)3 (0.88 mmol), and Er(CF3COO)3 (0.12 mmol) powder were introduced to a three-necked flask (100 ml) containing 8 ml of OM and 16 ml of OA at room temperature. After vigorous stirring for about 15 min, the mixture was then heated to 120 °C under the protection of nitrogen or argon atmosphere and maintained at this temperature for another 30 min under magnetic stirring to remove the oxygen and residual water. At this end, the mixture was totally clear forming a slight yellow color. The mixture was then heated slowly to 275 °C in the presence of argon atmosphere and maintained at the temperature for 30 min. After then, the solution was cooled down naturally to room temperature. Finally, NPs were then precipitated using excess ethanol and collected via centrifugation at 7000 rpm for 5 min. After washed with ethanol for several times, the as-prepared nanocrystals were dried in air at 70 °C overnight.
Preparation of NaGdF4:12%Er3+@ NaGdF4: x%Er3+ NPs
To prepare the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:x%Er3+ core/shell UCNPs (x = 0, 6, 8, 10, and 12), core NPs of NaGdF4 doped with 12% Er3+ ion concentration were firstly prepared following the procedure as described above. The procedure for the growth of shell on core is similar to the case of core except that 0.5-mmol core NPs re-dispersed in 4 ml cyclohexane were added simultaneously with rare earth trifluoroacetates to the mixture of OA and OM solution and the heating temperature was enhanced to 300 °C.
Characterization
Structures of the samples were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using X’TRA (Switzerland ARL) equipment provided with a Cu tube with Ka radiation at 1.54056 Å. The size and shape of the samples were observed by a JEM-2100 transmission electron microscope (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Luminescence spectra were obtained by the Acton SpectraPro Sp-2300 spectrophotometer with a photomultiplier tube equipped with 1540 nm as the excitation source. The fluorescence decay curves in visible region were recorded on a FLSP920 fluorescence spectrophotometer and using a Shimadzu R9287 photomultiplier (200–900 nm) as the detectors. All measurements were performed at room temperature.
Results and Discussion
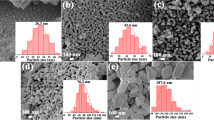
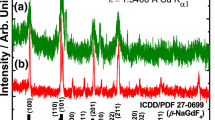
Figure 1 shows the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images and the size distribution of the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core NPs, NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/ inert-shell NPs, and NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell NPs, respectively. Obviously, all the as-prepared NPs are uniform in size and morphology. The NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core-only NPs consist of monodisperse NPs with an average diameter of ~12.5 nm. After coated with a shell, the diameter of the NPs tends to increase to about 175 nm (Fig. 1b, c). As disclosed by high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) images (inset in Fig. 1), all as-prepared NPs show their highly crystalline nature with the clear crystal fringes. XRD patterns (Fig. 2a) confirm that as-obtained NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core NPs possess cubic phase structures, in well agreement with the α-NaGdF4 (JCPDS card no. 27−0697) structure. Coating with a shell, the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell NPs and the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell NPs show hexagonal phase, and the identified diffraction peaks are also in well agreement with the XRD pattern of β-NaGdF4 (JCPDS card no. 27−0699). No obvious peak from other phases or impurities is observed [31].
XRD patterns of the a NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core nanoparticles, b NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell nanoparticles and NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell nanoparticles (C@x% for short). The bottom bars represent the standard α-NaGdF4 (JCPDS 27–0697) and β − NaGdF4 crystal data (JCPDS 27–0699), respectively.
Figure 3a shows the upconversion emission spectra of the core-only, active-core/ inert-shell, and active-core/active-shell NPs under the excitation at 1540 nm. All luminescence spectra exhibit the red, green, and NIR emission bands of Er3+, originating mainly from the following four transitions: 2H11/2→4I15/2 (528 nm), 4S3/2→4I15/2 (540 nm), 4F9/2→4I15/2 (660 nm), and 4I9/2→4I15/2 (810 nm). Compared with the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core-only NPs and the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core /inert-shell NPs, great enhancement of upconversion luminescence was obviously observed from the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ NPs. As seen in Fig. 3b, the sample of NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ NPs shows the strongest luminescence with shorter concentration step. Specifically, Fig. 4 presents the enhancement factors (which expresses the enhanced times) of all emission intensities of the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core-only NPs, NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/ inert-shell NPs, and NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:x%Er3+(x = 6, 8, 10, and 12) active-core/active-shell NPs. Compared with the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core-only NPs, the enhancement factor of the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell NPs is about 30 times larger. While when it comes to the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ @NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell NPs, a largest enhancement factor up to approximately 336 is observed. Comparing the as-obtained NPs with same size, the upconversion luminescence tends to decrease firstly and then gets the largest enhancement at 10 mol% to ~336 times, so the energy transfer reaction plays the main role in the huge enhancement of luminescence other than the effect of size [23]. Apparently, the NPs with an active shell realize much more effective upconversion luminescence than that with an inert shell.
As is known, the emission intensity of NPs will be enhanced by coating an inert shell over them, due to the confine of surface passivation [32]. The inert shell protects the ions in the core from non-radiative decay originate from surface defects. Therefore, the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ NPs capped with NaGdF4 gain an enhancement factor about 30. However, the luminescence of the NPs tends to decrease first when doped the Er3+ ions with 6 mol%. As reported before, the decrease is mainly caused by the less efficiency of sensitizers in shell than that in the core [25]. The luminescence of NPs reaches the highest value when the concentration value in the shell is 10 mol%. Higher doped Er3+ concentration strengthened the function of the active shell, leading to more efficient energy migration from the shell to the core. When the concentration of the shell comes to 10 mol%, the interaction of the Er3+ ions in the core and the shell may reach the peak as observed, bringing the largest enhancement of luminescence to 336 times. Other values of doping concentration are not beneficial for the higher emission intensity enhancement, suggesting that the higher or lower doping concentration may lead to the cross relaxations (CR) or the reduction of the luminescent activators [27, 32].
The effect of the shell structure on the intensity ratio of the green to red emission (IG/IR) is studied in Fig. 5a. With an inert shell, the value of IG/IR decreases to ~1.09. The reduction of non-radiative decay (caused by suppression of surface quenching) perhaps increased the probability of the CR process of Er3+ ions, resulting in the enhanced population on 4F9/2 level [33]. It is apparent that the IG/IR ratio is tuned by constructing the core–shell structure and changing the Er3+concentration in the shell. Essentially, the green and red emissions are mainly originated from the transitions of 2H11/2, 4S3/2→4I15/2, and 4F9/2→4I15/2 [34, 35]. Tuning the concentration of Er3+ in the shell directly changes the distance between the neighboring emitters, causing the cross relaxation to different extent [34]. And the emitter-doping concentration has been also verified to have a great influence in the ratio of green to red [36]. Consequently, it is easy to deduce that the as-observed changes of the green to red ratio of as-prepared NPs may mainly result from co-effect of concentration quenching and CR. And from the Fig. 5b, the bandwidth values of 540 and 660 nm about the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core NPs, NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell NPs, and NaGdF4:12%Er3+ @NaGdF4: x%Er3+(x = 6, 8, 10 and 12) active-core/active-shell NPs are presented. Coated with an inert or active shell, the bandwidth values with the full width at half maximum (FWHM) are all adjusted to lower values. The luminescent properties were well improved by tuning the FWHM values with core–shell structure.
Combined Fig. 3 with Fig. 5, one phenomenon can be found that the luminescence properties of as-obtained NPs exhibit an inhomogeneous increase mostly depending on the doping concentrations of Er3+ in the NaGdF4:Er3+ active shell. The phenomenon is also found in NaYF4:Nd3+/Yb3+/Ho3+@NaYF4:Nd3+/Yb3+ core/shell NPs under 808-nm excitation [27] and NaYF4:Er3+@NaYF4:Yb3+ active-core/active-shell NPs under 1540-nm excitation [28], probably owing to the combined interaction of energy transfer benefit, concentration quenching, and surface quenching effect of core–shell structures as estimation. When the concentration of Er3+ in the active shell comes to 10 mol%, the peak value can be observed through the luminescence spectra, largely due to the effect of successive ion layer absorption reaction.
As can be seen in Fig. 6, decay profiles of the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core NPs, the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell NPs, and the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@ NaGdF4: x%Er3+ (x = 6, 8, 10, and 12) active-core/active-shell NPs under 1540-nm excitation are proposed. The corresponding decay lifetimes can be calculated by the second order exponential curve fitting:
where I is the luminescence intensity, A 1 and A 2 are constants, t is the time, and τ 1 and τ 2 are the short and long lifetimes for exponential components, respectively. The average decay lifetime τ is determined by the formula:
The results of the calculation are all shown in Fig. 7. As can be seen, the obvious prolonged life can be experimentally observed by coating with a shell, indicating that the excited states of 2H11/2 (528 nm), 4S3/2 (540 nm), 4F9/2 (660 nm), and 4I9/2 (810 nm) are populated again through the energy transfer process between Er3+ ions. Comparing the values of the decay lifetime about the as-obtained NPs, one can find that while continuing to increase the Er3+ concentration higher than 6 mol%, the lifetime begin to decrease. The phenomenon can be explained by the fact that the probability of CR process is largely related to the ions concentration [37]. The profiles of excited state 2H11/2, 4S3/2, and 4I9/2 appear no obvious signal rising edge, indicating that they are populated by non-radiative relaxation [38]. Contrary to other decay curves in Fig. 6, the profile of NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ NPs at 660 nm presents a typical slow rising edge. This phenomenon is a direct evidence of an energy transfer upconversion process of state 4F9/2 [39]. As depicted in Fig. 7, the obvious prolonged lifetimes are experimentally observed at different degree, demonstrating that surface-quenching effects in both type of core/shell structure have been largely weaken. Comparably, the decay lifetimes of the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell NPs and the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell NPs under the 810 nm emission are smoother than other profiles, indicating that the population ions on the 4I9/2 state have less difference between different core–shell compositions.
As analyzed above, the energy transfer mechanism between the states of Er3+ ions is exhibited in Fig. 8. Four primary processes can be mainly used to explain these behaviors. The ground state absorption (GSA) of the 1540-nm pump wavelength directly populates the upper level 4I13/2. With the excitation of 4I13/2 state, the excited state absorption (ESA) process arises immediately, resulting in more high-lying levels to be excited. After coating with an inert shell, the surface quenching is largely confined and the depletion of low-lying levels is reduced to enhance the population of high-lying ones, bringing intensive luminescence (as seen in Fig. 3). At the same time, the low-lying levels are proved to be more susceptible to surface quenching than the higher ones [32]. Thus, the emission of red luminescence has a more obviously enhancement than the green upon the surface passivation effect take place due to the coating of inert shell [40]. The ratio of green to red changes from 1.44 to 1.09 after coating with an inert shell. With the epitaxial growth of an active shell, the ratio of green to red changes by adjusting Er3+ concentration among the shell. The ratio shows an inverse association with the enhancement luminescence of active-core/active-shell NPs (Fig. 4). The phenomenon indicates that the CR process of 4F3/2 + 4I15/2→4F9/2 + 4I13/2 is strengthened with the enhancement luminescence faster than the process of energy transfer upconversion (ETU). From the decay profile of 810 nm, the lifetime of the as-obtained NPs decreases firstly while doping the Er3+ ions into the shell, which is another direct evidence of the ETU process, populating the 4S3/2 and 2H11/2 state from the 4I9/2 state.
By further studying the temporal behavior of the red emission, one can find that the decay curves of 660 nm of the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell NPs and the NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell NPs exhibit a typical slow rising edge. As other work reported before, the rising edge is proved to be another evidence of CR as theoretical transients [39, 41]. Combined with the luminescence spectra, CR process of 4F3/2 + 4I15/2→4F9/2 + 4I13/2 makes large contribution to the population of the 4F9/2 state due to the higher and higher concentration of Er3+ in the shell, which also can be obtained from the calculated results of the lifetimes (Fig. 7). Besides, none emission of any state around 4F3/2 is found, proving the existence of CR. Consequently, under the co-effect of core/shell structure and optimized Er3+ concentration in shell, the energy transfer reaction is extremely improved, leading to the great luminescent enhancement of active-core/active-shell NPs.
Conclusions
In conclusion, a strategy was put forward to enhance the upconversion luminescence by forming active-core/active-shell structure with Er3+ ions single-doped NaGdF4 without any other lanthanide-doped ions. Hexagonal NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4:10%Er3+ active-core/active-shell NPs have been synthesized and present a significant intensive emission of the upconversion luminescence compared to NaGdF4:12%Er3+@NaGdF4 active-core/inert-shell and NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core-only NPs. Acting both as the emitter and the sensitizer, the luminescence of single Er3+-doped NaGdF4 UCNPs can be greatly enhanced by forming the structure of an active shell over the core. By the optimization of the concentration of Er3+ ions in the shell, the upconversion luminescent properties are greatly promoted and the enhancement of UC luminescence intensity is up to ~336 times greater than the NaGdF4:12%Er3+ core-only NPs, which is much larger than simply increasing the Er3+ concentration in NPs.
Abbreviations
- CR:
-
Cross relaxation
- ESA:
-
Excited state absorption
- ETU:
-
Energy transfer upconversion
- FWHM:
-
Full width at half maximum
- GSA:
-
Ground state absorption
- HRTEM:
-
High-resolution TEM
- NIR:
-
Near infrared
- NP:
-
Nanoparticle
- OA:
-
Oleic acid
- OM:
-
Oleylamine
- RE:
-
Rare earth
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- UC:
-
Upconversion
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Francois Auzel. Upconversion and Anti-Stokes Processes with f and d Ions in Solids. Chem. Rev. 2004; 104: 139−173
van der Ende BM, Aarts L, Meijerink A (2009) Lanthanide ions as spectral converters for solar cells. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:11081–11095
Wang H-Q, Batentschuk M, Osvet A, Pinna L, Brabec CJ (2011) Rare-earth ion doped up-conversion materials for photovoltaic applications. Adv Mater 23:2675–2680
Yang Y, Shao Q, Deng R, Wang C, Teng X, Cheng K, Cheng Z, Huang L, Liu Z, Liu X, Xing B (2012) In vitro and in vivo uncaging and bioluminescence imaging by using photocaged upconversion nanoparticles. Angew Chem-Int Edit 51:3125–3129
Wu X, Chen G, Shen J, Li Z, Zhang Y, Han G (2015) Upconversion nanoparticles: a versatile solution to multiscale biological imaging. Bioconjugate Chem 26:166–175
Qin W, Zhang D, Zhao D, Wang L, Zheng K (2010) Near-infrared photocatalysis based on YF3: Yb3+, Tm3+/TiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. Chem Commun 46:2304–2306
Wang F, Han Y, Lim CS, Lu Y, Wang J, Xu J, Chen H, Zhang C, Hong M, Liu X (2010) Simultaneous phase and size control of upconversion nanocrystals through lanthanide doping. Nature 463:1061–1065
Zhou Y, Han S-T, Chen X, Wang F, Tang Y-B, Roy VAL (2014) An upconverted photonic nonvolatile memory. Nat Commun 11:2003–2010
Vetrone F, Naccache R, Mahalingam V, Morgan CG, Capobianco JA (2009) The active-core/active-shell approach: a strategy to enhance the upconversion luminescence in lanthanide-doped nanoparticles. Adv Funct Mater 19:2924–2929
Chen G, Ohulchanskyy TY, Kumar R, Agren H, Prasad PN (2010) Ultrasmall monodisperse NaYF4:Yb3+/Tm3+ nanocrystals with enhanced near-infrared to near-infrared upconversion photoluminescence. ACS Nano 4:3163–3168
de Wild J, Rath JK, Meijerink A, van Sark WGJHM, Schropp REI (2010) Enhanced near-infrared response of a-Si:H solar cells with beta-NaYF4:Yb3+ (18%), Er3+ (2%) upconversion phosphors. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 94:2395–2398
Liu N, Qin W, Qin G, Jiang T, Zhao D (2011) Highly plasmon-enhanced upconversion emissions from Au@beta-NaYF4:Yb, Tm hybrid nanostructures. Chem Comm 47:7671–7673
Feng W, Sun LD, Yan CH (2009) Ag nanowires enhanced upconversion emission of NaYF4: Yb, Er nanocrystals via a direct assembly method. Chem Comm 29:4393–4395
Cheng Q, Sui J, Cai W (2012) Enhanced upconversion emission in Yb3+ and Er3+ codoped NaGdF4 nanocrystals by introducing Li+ ions. Nanoscale 4:779–784
Priyam A, Idris NM, Zhang Y (2012) Gold nanoshell coated NaYF4 nanoparticles for simultaneously enhanced upconversion fluorescence and darkfield imaging. J Mater Chem 22:960–965
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang X, Luo Y, Ren X, Zhao H, Wang X, Sun L, Yan C (2009) Near-infrared to visible upconversion in Er3+ and Yb3+ codoped Lu2O3 nanocrystals: enhanced red color upconversion and three-photon process in green color upconversion. J Phys Chem C 113:4413–4418
Chen G, Qiu H, Fan R, Hao S, Tan S, Yang C, Han G (2012) Lanthanide-doped ultrasmall yttrium fluoride nanoparticles with enhanced multicolor upconversion photoluminescence. J Mater Chem 22:20190–20196
Chen D, Yu Y, Huang F, Lin H, Huang P, Yang A, Wang Z, Wang Y (2012) Lanthanide dopant-induced formation of uniform sub-10 nm active-core/active-shell nanocrystals with near-infrared to near-infrared dual-modal luminescence. J Mater Chem 22:2632–2640
Chen M, Ma Y, Li M (2014) Facile one-pot synthesis of hydrophilic NaYF4:Yb, Er@NaYF4:Yb active-core/active-shell nanoparticles with enhanced upconversion luminescence. Mater Lett 114:80–83
Huang S, Gu L, Miao C, Lou Z, Zhu N, Yuan H, Shan A (2013) Near-infrared photocatalyst of Er3+/Yb3+ codoped (CaF2@TiO2) nanoparticles with active-core/active-shell structure. J Mater Chem A 1:7874–7879
Prorok K, Pawlyta M, Strek W, Bednarkiewicz A (2016) Energy migration up-conversion of Tb3+ in Yb3+ and Nd3+ codoped active-core/active-shell colloidal nanoparticles. Chem Mater 28:2295–2300
Qiu H, Yang C, Shao W, Damasco J, Wang X, Agren H, Prasad PN, Chen G (2014) Enhanced upconversion luminescence in Yb3+/Tm3+-codoped fluoride active core/active shell/inert shell nanoparticles through directed energy migration. Nanomaterials 4:55–68
Zhang Y, Wang F, Lang Y, Yin J, Zhang M, Liu X, Zhang D, Zhao D, Qin G, Qin W (2015) KMnF3:Yb3+, Er3+@KMnF3:Yb3+ active-core-active-shell nanoparticles with enhanced red upconversion fluorescence for polymer-based waveguide amplifiers operating at 650 nm. J Mater Chem C 3:9827–9832
Zhu W, Chen D, Lei L, Xu J, Wang Y (2014) An active-core/active-shell structure with enhanced quantum-cutting luminescence in Pr-Yb co-doped monodisperse nanoparticles. Nanoscale 6:10500–10504
Wu F, Liu X, Kong X, Zhang Y, Tu L, Liu K, Song S, Zhang H (2013) The real role of active-shell in enhancing the luminescence of lanthanides doped nanomaterials. Appl Phys Lett 102:24
Yang D, Li C, Li G, Shang M, Kang X, Lin J (2011) Colloidal synthesis and remarkable enhancement of the upconversion luminescence of BaGdF5:Yb3+/Er3+ nanoparticles by active-shell modification. J Mater Chem 21:5923–5927
Huang X, Lin J (2015) Active-core/active-shell nanostructured design: an effective strategy to enhance Nd3+/Yb3+ cascade sensitized upconversion luminescence in lanthanide-doped nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 3:7652–7657
Wang X, Xu T, Bu Y, Yan X (2016) Giant enhancement of upconversion emission in NaYF4:Er3+@NaYF4:Yb3+ active-core/active-shell nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6:22845–22851
Dong H, Sun L-D, Yan C-H (2015) Energy transfer in lanthanide upconversion studies for extended optical applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:1608–1634
Mai H-X, Zhang Y-W, Sun L-D, Yan C-R (2007) Highly efficient multicolor up-conversion emissions and their mechanisms of monodisperse NaYF4: Yb, Er core and core/shell-structured nanocrystals. J Phys Chem C 111:13730–13739
Zi L, Zhang D, De G (2016) Self-assembly NaGdF4 nanoparticles: phase controlled synthesis, morphology evolution, and upconversion luminescence properties. Mater Res Express 3:025009
Wang F, Wang J, Liu X (2010) Direct evidence of a surface quenching effect on size-dependent luminescence of upconversion nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Edit 49:7456–7460
Chen H, Lang Y, Zhao D, He C, Qin W (2015) Enhanced high-order upconversion luminescence of hexagonal phase NaYF4:Yb3+, Tm3+ crystals coated with homogeneous shell. J Fluor Chem 174:70–74
Liu X, Kong X, Zhang Y, Tu L, Wang Y, Zeng Q, Li C, Shi Z, Zhang H (2011) Breakthrough in concentration quenching threshold of upconversion luminescence via spatial separation of the emitter doping area for bio-applications. Chem Comm 47:11957–11959
Wang F, Liu X (2009) Recent advances in the chemistry of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanocrystals. Chem Soc Rev 38:976–989
Jia YQ (1991) Crystal radii and effective ionic-radii of the rare-earth ions. J Solid State Chem 95:184–187
Robbins DJ, Cockayne B, Lent B, Glasper JL (1976) The mechanism of 5D3-5D4 cross-relaxation in Y3Al5O12: Tb3+. Solid State Commun 20:673–676
Jia WY, Lim KS, Liu HM, Wang YY, Ju JJ, Yun SI, Fernandez FE, Yen WM (1996) Up-conversion of multi-site Er in LiNbO3 single-crystal fibers. J Lumin 190:66–67
Martin-Rodriguez R, Rabouw FT, Trevisani M, Bettinelli M, Meijerink A (2015) Upconversion dynamics in Er3+-doped Gd2O2S: influence of excitation power, Er3+ concentration, and defects. Adv Opt Mater 3:558–567
Schaefer H, Ptacek P, Zerzouf O, Haase M (2008) Synthesis and optical properties of KYF4: Yb, Er nanocrystals, and their surface modification with undoped KYF4. Adv Funct Mater 18:2913–2918
Miller MP, Wright JC (1978) Single site multiphonon and energy-transfer relaxation phenomena in BaF2-Er3+. J Chem Phys 68:1548–1562
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11404171, 11374162, 11504180), the Six Categories of Summit Talents of Jiangsu Province of China (2013-XCL-021), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (14KJB430020, TJ215009), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (NY215174).
Authors’ Contributions
XD and XW designed the experiments. XD carried out the synthesis and characterization of the samples, analyzed the results, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. XD, XW, and XY participated in the analyses of the results and discussion of this study. XW, LM, YB, and XY revised the manuscript and corrected the English. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Wang, X., Meng, L. et al. Enhance the Er3+ Upconversion Luminescence by Constructing NaGdF4:Er3+@NaGdF4:Er3+ Active-Core/Active-Shell Nanocrystals. Nanoscale Res Lett 12, 163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-1929-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-1929-8