Abstract
The nanocomposite materials of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphene oxide (PEDOT/GO), poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/MnO2 (PEDOT/MnO2), and poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphene oxide/MnO2 (PEDOT/GO/MnO2) were successfully prepared by facile and template-free solution method. The structure and morphology of nanonanocomposites were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet–visible absorption spectra (UV–vis), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), respectively. The catalytic activities of nanocomposites were investigated through the degradation processes of methylene blue (MB) solution under dark, UV light, and nature sunlight irradiation, respectively. The results displayed that nanocomposites were successfully synthesized, and PEDOT/GO had higher conjugation length and doped degree than pure PEDOT. However, the introduction of MnO2 could lead to the reduction of conjugation length and doped degree in PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites. The field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) analysis also showed that both MnO2 and GO had some effect on the morphology of nanocomposites. The catalytic activities of pure PEDOT and nanocomposites were in the order of PEDOT/GO/MnO2 > PEDOT/MnO2 > PEDOT/GO > pure PEDOT. Besides, the catalytic results also showed that the highest degradation efficiency of MB after 7 h occurred in the PEDOT/GO/MnO2 composite in three irradiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Dyes, pigments, and their causative compounds are difficult for industrialization since they are highly carcinogenic and undesirable in water as reported. Consequently, it is necessary to remove them from wastewater before discharge. Methylene blue (MB) is a water-soluble thiazine dye, commonly used for dyeing of silk, leather, plastics, and paper. On inhalation, MB can give rise to short periods of rapid or difficult breathing while ingestion through the mouth may cause hypertension and discomfort. To prevent harmful impacts of MB on receiving waters, the degradation of MB is of great importance in water treatment [1,2]. In recent years, catalysts have attracted much attention of scientists to removal of dyes [3,4]. Among the various catalysts, MnO2 is considered as one of the most outstanding metal oxides on new catalytic oxidation systems, due to its relative low price, chemical stability, and non-toxic property. By now, many efforts have been made on the application of MnO2 in battery materials, supercapacitor, and catalysts [5-10]. However, few studies have attention on the conductive polymers/MnO2 composites in water treatment. Among the conducting polymers, poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) has become commercially available conducting polymer because of its high conductivity, effective thermal stability, fast charge/discharge ability, low-oxidation potential, and high cycling stability [11-13]. In addition, delocalized conjugated structures of conductive polymers have been proven to arouse a rapid photoinduced charge separation and decrease the charge recombination rate in electron-transfer processes [14,11]. Until now, many chemical methods have been reported for the formation of conducting polymer/MnO2 composites. Commonly, monomers are always oxidized to obtain the conducting polymer, and KMnO4 is reduced to give MnO2. Despite the obvious advantages of simplicity and reproducibility in this synthetic method, the morphology of such composites and the size of MnO2 particles are normally hard to control. More interestingly, it has been recently revealed that conducting polymers themselves show redox activity toward KMnO4, where KMnO4 is always reduced to MnO2 [15]. As the redox reactions occur on the surfaces of conducting polymers, MnO2 will prefer to adsorb on the surfaces of the conducting polymer. Recently, graphene oxide (GO) has received intensive attention owing to the fascinating mechanical, electrical, thermal, and optical properties. In comparison with other carbon materials, GO has the perfect sp2 hybrid carbon nanostructure and various oxygen groups including epoxide, hydroxyl, carbonyl, and carboxyl groups. In addition, the conjugation of GO with semiconductor solid particles results in catalysts with improved charge separation, reduced recombination of the photogenerated electron–hole pairs, increased specific surface area, and an adequate quantity of adsorption sites, which could lead to the enhancement of degradation efficiency of wastewater [16-19]. On account of the abovementioned advantages, the reasonable combination of PEDOT, GO, and MnO2 would produce some novel composites with excellent catalytic performance.
Herein, we report the synthesis of binary and ternary nanocomposites of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphene oxide (PEDOT/GO), poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/MnO2 (PEDOT/MnO2), and poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphene oxide/MnO2 (PEDOT/GO/MnO2) via facile and template-free solution process. The structural and morphological properties of nanocomposites were investigated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet–visible absorption spectra (UV–vis), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), X-ray diffraction, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Furthermore, nanocomposites were tested as catalysts for removal of MB from aqueous solution under different light sources.
Methods
Materials
3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) was obtained from Shanghai Aladdin Reagent Company (Shanghai, China), and it was purified by distillation under reduced pressure and stored in a refrigerator prior to use. All other chemicals and solvents, including FeCl3 · 6H2O, potassium permanganate (KMnO4), ethanol, and chloroform, were used as received without further purification.
Preparation of the PEDOT and PEDOT/GO
The procedure for synthesis of PEDOT was as follows: the pure PEDOT polymer was prepared by mixing a 5.0 mL of 14.2 wt.% EDOT alcoholic solution and 20 mL FeCl3 · 6H2O (2.0 M) aqueous solution. The reaction system was maintained under magnetic stirring for 24 h. Then, the resulting mixture was filtered, washed, and dried at 60°C for 12 h.
The procedure for synthesis of PEDOT/GO composite was as follows: 0.04 g GO was dissolved in 20 mL FeCl3 · 6H2O (2.0 M) aqueous solution; then, the PEDOT/GO composite was prepared by mixing a 5.0 mL of 14.2 wt.% EDOT alcoholic solution and FeCl3 · 6H2O aqueous solution. The reaction system was maintained under magnetic stirring for 24 h. Then, the resulting mixture was filtered, washed, and dried at 60°C for 12 h.
Preparation of PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2
The procedure for preparation of PEDOT/MnO2 nanocomposites was as follows: the incorporation of MnO2 was carried out by soaking 0.08 g PEDOT powders into KMnO4 aqueous solution (0.16 g, 10 mM). Then, the reaction system was maintained under magnetic stirring at room temperature for 10 min. The products were further rinsed several times with deionized water and dried under vacuum at 60°C for 24 h. PEDOT/GO/MnO2 composite was synthesized by the same method but only used PEDOT/GO powders instead of PEDOT.
Characterization techniques
The Fourier transform infrared spectra of the samples were measured on a BRUKER EQUINOX-55 Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (Bruker Optics, Billerica, MA, USA) at a resolution of 4 cm−1 using the KBr technique. UV–vis spectra of the samples were recorded on a UV-visible spectrophotometer (UV4802, Unico, Dayton, NJ, USA). The XRD patterns have been obtained by using a Bruker AXS D8 diffractometer (Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA), and the scan range was 10° to 80°, with monochromatic Cu-Ka radiation source (λ = 0.15418 nm). The elemental percentages of samples were measured on energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, which was taken on a Leo1430VP microscope (Carl Zeiss Inc., Oberkochen, Germany) with operating voltage 5 kV. The process of EDX measures were carried out with a pellet which was pressed at 200 MPa and then adhered to copper platens. Morphology and microstructure of the samples were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM Hitachi S-4800, Hitachi Ltd., Chiyoda-ku, Japan).
Degradation experiments of methylene blue
The catalytic activity of pure PEDOT and nanocomposites were performed using MB dyes as degraded materials in quartz tubes under dark, UV light, and natural sunlight irradiation. Of catalysts (PEDOT), 20 mg was shaken in MB solution (50 mL) and stirred for 7 h. After degradation of dye, the catalysts were removed by centrifugation. FSL MW1-Y15 (Foshan Electrical and Lighting Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China) was used as the irradiation source (λ = 254 nm) located in a light infiltrated chamber. The degradation study of PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites was conducted by the same method.
Results and discussion
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
Figure 1 shows the FTIR spectra of PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites. As shown in Figure 1, the characteristic absorption bands of the PEDOT and PEDOT/GO are at 1,510, 1,316, 1,176, 1,140, 1,044, 921, 831, and 704 cm−1, respectively. The bands of 1,510, 1,316, 1,176, 1,140, and 1,044 cm−1 are assigned to the aromatic C = C stretching in benzene ring of polythiophene and the C-O-C bond stretching in ethylenedioxy group, respectively [20]. The presence of C-S-C bond in the thiophene ring is indicated by the bands at 921, 831, and 704 cm−1 [21]. Moreover, several absorption bands around 3,395 and 1,630 cm−1 are observed in PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, which can be attributed to stretching and bending vibrations of the -OH group of crystal and adsorbed water molecules, respectively [22]. In addition, the band of Mn − O and Mn − O − Mn vibrations at 510 cm−1 is observed in the case of PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, which supports that the presence of MnO2 in nanocomposites [23].
UV–vis spectra
Figure 2 shows the UV–vis absorption spectra of PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, respectively. As can be seen in Figure 2, pure PEDOT displays a broad absorption band, starting at ca.450 nm and extending into the mid IR region, which is very similar to that of previously reported PEDOT [12]. Compared with pure PEDOT, the higher intensity of absorption peaks near 700 to 1,000 nm is observed in the case of PEDOT/GO nanocomposites, which corresponds to the polymer having a longer conjugation length with greater order [12,24]. This result suggests that PEDOT/GO nanocomposites have the higher conjugation length and doped degree than pure PEDOT. However, the introduction of MnO2 in PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites will lead to the reduction of conjugation length and doped degree. Further comparison indicates that PEDOT/GO/MnO2 has the higher conjugation length and doped degree than that of PEDOT/MnO2. Moreover, a broad band between 400 and 700 nm with λ max at 500 nm is observed in PEDOT/GO/MnO2, which can be attributed to the π-π* transition of the thiophene ring [25].
Field emission scanning electron microscope
Figure 3 shows the FESEM images of PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, respectively. As depicted in Figure 3a,b,c,d, pure PEDOT exhibits coral-like morphology and PEDOT/MnO2 shows flower-like morphology. After the formation of PEDOT/GO and PEDOT/GO/MnO2, the presence of thin-layered GO can be seen in the nanocomposites and GO makes solely coral-like morphology of PEDOT connected with each other to form the porous structure. In addition, many flocculent structures are clearly observed on the surface of PEDOT/GO and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, suggesting the strong interactions between PEDOT and GO in the nanocomposite. The above results show that both MnO2 and GO have some effect on the morphology of nanocomposites.
X-ray diffraction
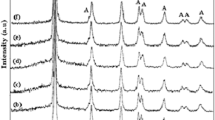
Figure 4 shows the XRD patterns of PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, respectively. As shown in Figure 4, the pure PEDOT and PEDOT/GO display broad diffraction peaks with low intensity at 2θ = 26°, which can be attributed to the intermolecular spacing of polymer backbone or assigned to the (020) reflection [26]. Besides, two diffraction peaks at 2θ = 37° (211) and 66° (002) indexed to MnO2 (JCPDS No. 44–0141) are observed in the case of PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, suggesting the successful incorporation of MnO2 in nanocomposites [27,28]. However, the XRD pattern of MnO2 in the nanocomposites showed broad and low peaks, revealing a poorly crystalline phase of MnO2. Besides, the diffraction peaks from GO are difficult to detect in the PEDOT/GO and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, which may be due to a low mass ratio.
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
To study the element percentage of Mn in PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites, EDX results of nanocomposites are presented in Figure 5. The results show that the percentage of Mn in PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites are 30.32 wt.% and 27.35 wt.%, respectively. Furthermore, the element of Cl and Fe are observed in nanocomposites, which should be resulted from the doping agent of FeC14 −.
Degradation experiments of methylene blue
The degradation of MB dyes was performed in the presence of pure PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites as catalysts under dark, UV light, and sunlight sources, respectively. The degradation efficiency of samples (R, %) was calculated by the following equation: R = [C o − C/C o] (where C o represents the initial concentration of dye, C represents the concentration of dye after a certain irradiation time, respectively).
Figure 6 shows the degradation spectra of MB in the presence of pure PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites under dark, respectively. The time profiles of MB degradation with the pure PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/ MnO2 nanocomposites under dark were shown in Figure 7. As can be seen in Figures 6 and 7, the degradation efficiencies of the MB dye by PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites are 9.9%, 36.5%, 86.2%, and 92.7% under dark, respectively. According to the SEM analysis, the pure PEDOT exhibits coral-like morphology with a smaller pore size. With the addition of GO, the PEDOT/GO displays flocculent structures with a larger pore size, which is beneficial for the physical adsorption of MB molecule. Furthermore, due to formation of π-π stacking between MB and aromatic regions of the graphene oxide in the PEDOT/GO composite, the physical adsorption of MB molecules can be promoted [16,29]. It should be noted that specific area of pure PEDOT is higher than PEDOT/GO, and the high specific area can enhance the adsorbability of MB by electrostatic interaction between the polymer chains and MB molecules [30]. However, compared with the pure PEDOT (9.9%), the higher degradation efficiency of MB solution occurred in PEDOT/GO (36.5%) composite. This result shows that the presence of GO in PEDOT/GO composite can be the main factor for improving the physical adsorption of MB molecules, suggesting that the GO has higher adsorbability for MB than that of PEDOT. Moreover, the degradation of MB by pure PEDOT and PEDOT/GO composite is physical adsorptive removal of MB molecules. However, the higher degradation efficiencies of MB solution are observed in the case of PEDOT/MnO2 (86.2%) and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 (92.7%) nanocomposites than that of pure PEDOT (9.9%) and PEDOT/GO (36.5%) nanocomposite. As shown in Figure 3, a lot of wrinkles are observed on the flower-like morphology of PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 displays flocculent structures with a larger pore size than that of PEDOT/GO. Based on the discussion about the effect of morphology of pure PEDOT and PEDOT/GO on the physical adsorptive removal of MB molecules, it is clear that the flower-like morphology of PEDOT/MnO2 and flocculent structure of PEDOT/GO/MnO2 are beneficial for the physical adsorption of MB molecule on the surface of nanocomposites. However, if the physical adsorptive removal of MB molecules is the decisive factor for enhancing the degradation efficiency of MB solution, the degradation efficiency of MB is impossible to be 86.2% and 92.7% for PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2, respectively. Thus, the presence of MnO2 in both of PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 composites will be the most important factor for determining the degradation efficiency of MB. Previous studies show that the MnO2 is one of the effective catalysts for degradation of MB, which can be attributed to the formation of hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl groups on the surface of MnO2 and the nitrogen atoms of MB [31]. Therefore, it can be concluded that the presence of MnO2 in PEDOT/MnO2 and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 plays an important role on the enhancement of degradation of MB under dark.
Figure 8a,b shows time profiles of MB degradation with the pure PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites under UV light and sunlight sources, respectively. As can be seen in Figure 8a,b, the degradation efficiency of the MB in the presence of pure PEDOT, PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites are 21.2%, 72.9%, 93.3%, and 97.1% under UV light and 54.7%, 81.4%, 95.7%, and 98.9 % under natural sunlight, respectively. One can clearly see that the degradation efficiency of the MB in the presence of pure PEDOT under natural sunlight (54.7%) was much higher than under the UV light (21.2%). This result may be due to the pure PEDOT that can absorb the visible light and produces an electron (e−), which will promote the charge separation and the formation of oxyradicals (O2, HO2, ·OH) [32]. Consequently, the high amounts of oxyradicals result in high degradation efficiency of MB under natural sunlight. Besides, it also indicates that the degradation efficiency of the MB in the presence of PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites under natural sunlight were much higher than that of nanocomposites under the UV light. Furthermore, GO as an excellent electron acceptor and transporter could reduce the recombination of charge carriers and enhance the catalytic activity [33,34], and this will be the main reason for higher degradation efficiency of the MB for PEDOT/GO than that of pure PEDOT under UV light and natural sunlight illumination. A further comparison displays that the highest degradation efficiency of the MB is observed in the case of PEDOT/GO/MnO2 composite under dark, UV light, and natural sunlight, respectively, suggesting that the degradation efficiency of MB solution influenced by the synergic effects of PEDOT, GO, and MnO2.
Conclusions
In this work, the composite materials of PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 were successfully synthesized by facile and template-free solution method. The results showed that nanocomposites were successfully prepared. Moreover, PEDOT/GO had higher conjugation length and doped degree than pure PEDOT, which may be due to the positive effect of GO on the degree of polymerization of PEDOT. And the results also displayed that both GO and MnO2 had some effect on the morphology of nanocomposites. Due to pure PEDOT can absorb the visible light and promote the formation of oxyradicals, the degradation efficiency of the MB in the presence of PEDOT and nanocomposites under natural sunlight were much higher than under UV light. Although the physical adsorption of nanocomposites has some effect on the degradation of the MB, the catalysis effect is the main factor to enhance the degradation efficiency of the MB. Among pure PEDOT and nanocomposites, the highest degradation efficiency of MB was observed in the case of PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites under different light sources. This phenomenon can be attributed to the hydrogen bonding between surface hydroxyl groups of MnO2 and the nitrogen atoms of MB. Another reason may be due to the formation of π-π stacking between MB and aromatic regions of the graphene oxide, and graphene oxide as an excellent electron acceptor and transporter could reduce the recombination of charge carriers and enhance the catalytic activity. That is to say, the synergetic effects between PEDOT and MnO2 as well as GO would be combined together to affect the catalytic activity of nanocomposites.
References
Thanh DV, Chen HC, Li LJ, Chu CW, Wei KH. Plasma electrolysis allows the facile and efficient production of graphite oxide from recycled graphite. RSC Adv. 2013;3:17402–10.
Chowdhury S, Balasubramanian R. Graphene/semiconductor nanocomposites (GSNs) for heterogeneous photocatalytic decolorization of wastewaters contaminated with synthetic dyes: a review. Appl Catal. 2014;160:307–24.
Xiong P, Wang L, Sun X, Xu B, Wang X. Ternary titania-cobalt ferrite-polyaniline nanocomposite: a magnetically recyclable hybrid for adsorption and photodegradation of dyes under visible light. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52:10105–13.
Chen TY, Chang YH, Hsu CL, Wei KH, Chiang CY, Li LJ. Comparative study on MoS2 and WS2 for electrocatalytic water splitting. Int J of Hydrogen Energ. 2013;38:12302–9.
Yoon SB, Kim KB. Effect of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) on the pseudocapacitive properties of manganese oxide (MnO2) in the PEDOT/MnO2/multiwall carbon nanotube (MWNT) composite. Electrochim Acta. 2013;106:135–42.
Duay J, Gillette E, Liu R, Lee SB. Highly flexible pseudocapacitor based on freestanding heterogeneous MnO2/conductive polymer nanowire arrays. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2012;14:3329–37.
Sharma RK, Zhai L. Multiwall carbon nanotube supported poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/manganese oxide nano-composite electrode for super-capacitors. Electrochim Acta. 2009;54:7148–55.
Chen R, Yu J, Xiao W. Hierarchically porous MnO2 microspheres with enhanced adsorption performance. J Mater Chem. 2013;1:11682.
Qu J, Shi L, He C, Gao F, Li B, Zhou Q, et al. Highly efficient synthesis of graphene/MnO2 hybrids and their application for ultrafast oxidative decomposition of methylene blue. Carbon. 2014;66:485–92.
Cheng G, Yu L, Lin T, Yang R, Sun M, Lan B, et al. A facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of β-MnO2 nanopincers and their catalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Solid State Chem. 2014;217:57–63.
Eren E, Celik G, Uygun A, Tabačiarová J, Omastová M. Synthesis of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/titanium dioxide nanocomposites in the presence of surfactants and their properties. Synth Met. 2012;162:1451–8.
Abdiryim T, Ubul A, Jamal R, Xu F, Rahman A. Electrochemical properties of the poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/single-walled carbon nanotubes composite synthesized by solid-state heating method. Synth Met. 2012;162:1604–8.
Wang W, Lei W, Yao T, Xia X, Huang W, Hao Q, et al. One-pot synthesis of graphene/SnO2/PEDOT ternary electrode material for supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta. 2013;108:118–26.
Wang Y, Xu J, Zong W, Zhu Y. Enhancement of photoelectric catalytic activity of TiO2 film via polyaniline hybridization. J Solid State Chem. 2011;184:1433–8.
Liu R, Duay J, Lee SB. Redox exchange induced MnO2 nanoparticle enrichment in poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanowires for electrochemical energy storage. ACS Nano. 2010;4:4299–307.
Zhang H, Lv X, Li Y, Wang Y, Li J. P25-graphene composite as a high performance photocatalyst. ACS Nano. 2009;4:380–6.
Bradder P, Ling SK, Wang S, Liu S. Dye adsorption on layered graphite oxide. J Chem Eng Data. 2010;56:138–41.
Lp W, Zhang L, Lu L, Duan X, Xu J, Nie T. Graphene oxide doped poly(hydroxymethylated-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): enhanced sensitivity for electrochemical determination of rutin and ascorbic acid. Chinese J Polym Sci. 2014;32:1019–31.
Cha I, Lee EJ, Park HS, Kim JH, Kim YH, Song C. Facile electrochemical synthesis of polydopamine-incorporated graphene oxide/PEDOT hybrid thin films for pseudocapacitive behaviors. Synth Met. 2014;195:162–6.
Shin HJ, Jeon SS, Im SS. CNT/PEDOT core/shell nanostructures as a counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. Synth Met. 2011;161:1284–8.
Sindhu S, Siju C, Sharma S, Rao K, Gopal E. Optical, electrochemical and morphological investigations of poly(3, 4-propylenedioxythiophene)-sultone (PProDOT-S) thin films. Bull Mater Sci. 2012;35:611–6.
Mohammed-Ziegler I. Selective complex formation of some chromogenic calix[4]arene derivatives detected by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy 2. Solid experiments. Spectrochim Acta Part A. 2003;59:3239–51.
Ma H, Shen J, Shi M, Yan B, Li N, Ye M. Facile and template-free preparation of α-MnO2 nanostructures and their enhanced adsorbability. Mater Res Bull. 2011;46:1461–6.
Yamamoto T, Shimizu T, Kurokawa E. Doping behavior of water-soluble π-conjugated polythiophenes depending on pH and interaction of the polymer with DNA. React Funct Polym. 2000;43:79–84.
Osman Y, Jamal R, Rahman A, Xu F, Ali A, Abdiryim T. Comparative study on poly(3,4-propylenedioxythiophene)/TiO2 nanocomposites synthesized by mechanochemical and chemical solution methods. Synth Met. 2013;179:54–9.
Jo SH, Lee YK, Yang JW, Jung WG, Kim JY. Carbon nanotube-based flexible transparent electrode films hybridized with self-assembling PEDOT. Synth Met. 2012;162:1279–84.
Lv Y, Li H, Xie Y, Li S, Li J, Xing Y, et al. Facile synthesis and electrochemical properties of MnO2/carbon nanotubes. Particuology. 2014;15:34–8.
Devaraj S, Munichandraiah N. Effect of crystallographic structure of MnO2 on its electrochemical capacitance properties. J Phys Chem C. 2008;112:4406–17.
Ng YH, Iwase A, Kudo A, Amal R. Reducing graphene oxide on a visible-light BiVO4 photocatalyst for an enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. J Phys Chem Let. 2010;1:2607–12.
Radoičić M, Šaponjić Z, Janković IA, Ćirić-Marjanović G, Ahrenkiel SP, Čomor MI. Improvements to the photocatalytic efficiency of polyaniline modified TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl Catal. 2013;136–137:133–9.
Cao J, Mao Q, Shi L, Qian Y. Fabrication of γ-MnO2/α-MnO2 hollow core/shell structures and their application to water treatment. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:16210.
Abdiryim T, Ali A, Jamal R, Osman Y, Zhang Y. A facile solid-state heating method for preparation of poly(3,4-ethelenedioxythiophene)/ZnO nanocomposite and photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014;9:1–8.
Wang W, Yu J, Xiang Q, Cheng B. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of hierarchical macro/mesoporous TiO2-graphene composites for photodegradation of acetone in air. Appl Catal B Environ. 2012;119–120:109–16.
Ameen S, Seo H-K, Shaheer Akhtar M, Shin HS. Novel graphene/polyaniline nanocomposites and its photocatalytic activity toward the degradation of rose Bengal dye. Chem Eng J. 2012;210:220–8.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21264014, No. 21464014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
TA conceived the study, carried out data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. LZ carried out the sample preparation and the experimental measure. RJ participated in the study of material structures and the data analysis. QZ and MCW coordinated the research and revised and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
To view a copy of this licence, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Jamal, R., Zhao, Q. et al. Preparation of PEDOT/GO, PEDOT/MnO2, and PEDOT/GO/MnO2 nanocomposites and their application in catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Nanoscale Res Lett 10, 148 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0859-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0859-6